15.2 並查集
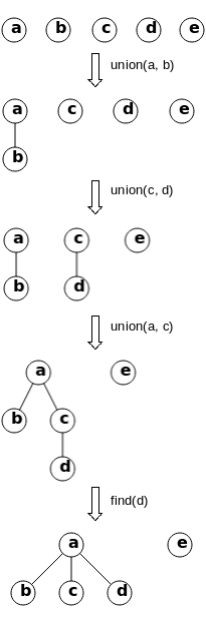
並查集(union-find, disjoint set)是一種用於動態連通性問題的數據結構,可以高效地實現動態連接兩個點,並快速判斷兩個點是否連通。假設有 n 個節點,我們初始化時將所有節點的父節點設為自身;每次需要連接節點 i 和 j 時,可以將秩較小一方的父節點標記為另一方(按秩合併);每次需要查詢兩個節點是否相連時,可以查找 i 和 j 的祖先是否相同,並通過路徑壓縮減少祖先層級,從而加速後續的查詢操作。
684. Redundant Connection
題目描述
在無向圖中找出一條邊,移除後該圖可以成為一棵樹(即無向無環圖)。如果有多個解,返回原陣列中位置最靠後的那條邊。
輸入輸出範例
輸入是一個二維陣列,表示所有的邊(對應的兩個節點);輸出是一個一維陣列,表示需要移除的邊(對應的兩個節點)。
Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
1
/ \
2 - 3
Output: [2,3]
題解
由於需要判斷是否兩個節點被重複連通,我們可以使用並查集來解決此類問題。以下為實現細節:
- C++
- Python
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
n_ = edges.size();
id_ = vector<int>(n_);
depth_ = vector<int>(n_, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n_; ++i) {
id_[i] = i;
}
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int i = edge[0], j = edge[1];
if (linked(i - 1, j - 1)) {
return vector<int>{i, j};
}
connect(i - 1, j - 1);
}
return vector<int>();
}
private:
int find(int i) {
// 路徑壓縮。
while (i != id_[i]) {
id_[i] = id_[id_[i]];
i = id_[i];
}
return i;
}
void connect(int i, int j) {
i = find(i), j = find(j);
if (i == j) {
return;
}
// 按秩合併。
if (depth_[i] <= depth_[j]) {
id_[i] = j;
depth_[j] = max(depth_[j], depth_[i] + 1);
} else {
id_[j] = i;
depth_[i] = max(depth_[i], depth_[j] + 1);
}
}
bool linked(int i, int j) { return find(i) == find(j); }
int n_;
vector<int> id_;
vector<int> depth_;
};
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.n = 0
self.id = None
self.depth = None
def find(self, i: int) -> int:
# 路徑壓縮。
while i != self.id[i]:
self.id[i] = self.id[self.id[i]]
i = self.id[i]
return i
def connect(self, i: int, j: int):
i = self.find(i)
j = self.find(j)
if i == j:
return
# 按秩合併。
if self.depth[i] <= self.depth[j]:
self.id[i] = j
self.depth[j] = max(self.depth[j], self.depth[i] + 1)
else:
self.id[j] = i
self.depth[i] = max(self.depth[i], self.depth[j] + 1)
def linked(self, i: int, j: int) -> bool:
return self.find(i) == self.find(j)
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
self.n = len(edges)
self.id = list(range(self.n))
self.depth = [1] * self.n
for i, j in edges:
if self.linked(i - 1, j - 1):
return [i, j]
self.connect(i - 1, j - 1)
return []
複雜度分析
- 時間複雜度: ,其中 是阿克曼函數的反函數,幾乎可以看作常數。
- 空間複雜度: ,儲存
id和depth陣列。