15.2 Union-Find
Union-Find (disjoint set) is a data structure used for dynamic connectivity problems. It efficiently connects two points and determines whether two points are connected. Given n nodes, we initialize the parent of each node to itself. To connect nodes i and j, we attach the smaller rank's parent to the larger rank's parent (union by rank). To check if two nodes are connected, we find their ancestors and determine if they are the same, applying path compression to speed up subsequent queries.
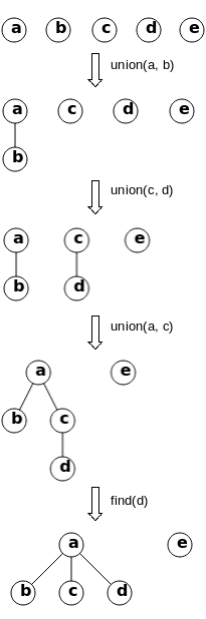
union merges two sets by rank, and find retrieves a node's ancestor while compressing paths.684. Redundant Connection
Problem Description
In an undirected graph, find an edge that, when removed, leaves the graph as a tree (i.e., acyclic and connected). If there are multiple solutions, return the edge appearing last in the input.
Input and Output Example
The input is a 2D array representing all edges (pairs of nodes), and the output is a 1D array representing the edge to remove.
Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
1
/ \
2 - 3
Output: [2,3]
Solution Explanation
Since we need to determine whether two nodes are repeatedly connected, we can solve this problem using the Union-Find data structure. The detailed implementation is as follows:
- C++
- Python
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
n_ = edges.size();
id_ = vector<int>(n_);
depth_ = vector<int>(n_, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n_; ++i) {
id_[i] = i;
}
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int i = edge[0], j = edge[1];
if (linked(i - 1, j - 1)) {
return vector<int>{i, j};
}
connect(i - 1, j - 1);
}
return vector<int>();
}
private:
int find(int i) {
// Path Compression
while (i != id_[i]) {
id_[i] = id_[id_[i]];
i = id_[i];
}
return i;
}
void connect(int i, int j) {
i = find(i), j = find(j);
if (i == j) {
return;
}
// Union by Rank
if (depth_[i] <= depth_[j]) {
id_[i] = j;
depth_[j] = max(depth_[j], depth_[i] + 1);
} else {
id_[j] = i;
depth_[i] = max(depth_[i], depth_[j] + 1);
}
}
bool linked(int i, int j) { return find(i) == find(j); }
int n_;
vector<int> id_;
vector<int> depth_;
};
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.n = 0
self.id = None
self.depth = None
def find(self, i: int) -> int:
# Path Compression
while i != self.id[i]:
self.id[i] = self.id[self.id[i]]
i = self.id[i]
return i
def connect(self, i: int, j: int):
i = self.find(i)
j = self.find(j)
if i == j:
return
# Union by Rank
if self.depth[i] <= self.depth[j]:
self.id[i] = j
self.depth[j] = max(self.depth[j], self.depth[i] + 1)
else:
self.id[j] = i
self.depth[i] = max(self.depth[i], self.depth[j] + 1)
def linked(self, i: int, j: int) -> bool:
return self.find(i) == self.find(j)
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
self.n = len(edges)
self.id = list(range(self.n))
self.depth = [1] * self.n
for i, j in edges:
if self.linked(i - 1, j - 1):
return [i, j]
self.connect(i - 1, j - 1)
return []